Windows Standard Deployment
This article will walk you through the procedure to install and deploy Bitwarden to your own Windows server. Bitwarden can also be installed and deployed on Linux and macOS machines. Please review Bitwarden software release support documentation.
System specifications
Minimum | Recommended | |
|---|---|---|
Processor | x64, 1.4GHz | x64, 2GHz Dual Core |
Memory | 6GB RAM | 8+ GB RAM |
Storage | 76GB | 90GB |
Docker Version | Engine 26+ and Compose | Engine 26+ and Compose |
ª - Docker Compose can be installed via Docker Desktop, which includes Engine and Compose.
Nested virtualization
Running Bitwarden on Windows Server requires use of nested virtualization. Please check your Hypervisor's documentation to find out if nested virtualization is supported and how to enable it.
tip
If you are running Windows Server as an Azure VM, we recommend a Standard D2s v3 Virtual Machine running Windows Server 2022, which meets all system requirements including support for nested virtualization. You will also need to select Security Type: Standard rather than the default Trusted launch virtual machines.
TL;DR
The following is a summary of the installation procedure in this article. Links in this section will jump to detailed Installation procedure sections:
Configure your domain. Set DNS records for a domain name pointing to your machine, and open ports 80 and 443 on the machine.
Install and setup Docker Desktop on your machine.
Create a Bitwarden user & directory from which to complete the installation.
Retrieve an installation id and key from https://bitwarden.com/host for use in installation.
For more information, see What are my installation id and installation key used for?
Install Bitwarden on your machine.
Configure your environment by adjusting settings in
\bwdata\env\global.override.env.tip
At a minimum, configure the
globalSettings__mail__smtp...variables to setup an email server for inviting and verifying users.Test your installation by opening your configured domain in a web browser.
Once deployed, we recommend regularly backing up your server and checking for system updates.
Installation procedure
note
Using the PowerShell ISE to run PowerShell commands will cause the Bitwarden installation to fail. Completing a successful install will require PowerShell.
Configure your domain
By default, Bitwarden will be served through ports 80 (http) and 443 (https) on the host machine. Open these ports so that Bitwarden can be accessed from within and/or outside of the network. You may opt to choose different ports during installation.
tip
If you are using Windows Firewall, Docker Desktop for Windows will not automatically add an exception for itself in Windows Firewall. Add exceptions for TCP ports 80 and 443 (or chosen alternative ports) to prevent related errors.
We recommend configuring a domain name with DNS records that point to your host machine (for example, bitwarden.example.com), especially if you are serving Bitwarden over the internet.
Setup Docker Desktop
Bitwarden will be deployed and run on your machine using an array of Docker containers. Bitwarden can be run with any Docker edition or plan. Evaluate which edition is best for your installation.
Deployment of containers is orchestrated using Docker Compose. Docker Compose can be installed via Docker Desktop, which includes Engine and Compose.
Install Docker Desktop for Engine and Compose.
During this setup, you must uncheck the Use WSL2 instead of Hyper-V (recommended) option. After installing, open Docker Desktop and select Settings and then Resources. Bitwarden requires at least 4GB of RAM allocated to Docker Desktop. This setting will dedicate the RAM from Windows exclusively to Docker. As a result, setting this value too high may cause instability within Windows.
Create Bitwarden local user & directory
Open PowerShell and create a Bitwarden local user by running the following commands:
BashPS C:\> $Password = Read-Host -AsSecureStringAfter running the above command, enter the desired password in the text input dialog. After specifying a password, run the following:
BashNew-LocalUser "Bitwarden" -Password $Password -Description "Bitwarden Local Admin"As the newly created user, create a Bitwarden folder under C:\:
BashPS C:\> mkdir Bitwarden
In Docker Desktop, navigate to Settings → Resources → File Sharing and add the created directory (C:\Bitwarden) to the Resources list. Select Apply & Restart to apply your changes.
note
The Bitwarden user must be added to the docker-users group. See Docker's documentation to learn how.
We recommend logging in as the newly created user before completing all subsequent procedures in this document.
Install Bitwarden
Bitwarden provides a PowerShell Cmdlet file (.ps1) for easy installation on Windows machines. Complete the following steps to install Bitwarden using the Cmdlet:
tip
If you have created a Bitwarden user & directory, complete the following as the Bitwarden user.
Navigate to the created directory:
Bashcd C:\BitwardenRun the following command to download the Bitwarden installation script (
bitwarden.ps1):BashInvoke-RestMethod -OutFile bitwarden.ps1 -Uri "https://func.bitwarden.com/api/dl/?app=self-host&platform=windows"Run the installer script using the following command:
Bash.\bitwarden.ps1 -installComplete the prompts in the installer:
Enter the domain name for your Bitwarden instance:
Typically, this value should be the configured DNS record.
Do you want to use Let's Encrypt to generate a free SSL certificate? (y/n):
Specify
yto generate a trusted SSL certificate using Let's Encrypt. You will be prompted to enter an email address for expiration reminders from Let's Encrypt. For more information, see Certificate Options.Alternatively, specify
nand use the do you have a SSL certificate to use? option.Enter your installation id:
Retrieve an installation id using a valid email at https://bitwarden.com/host. For more information, see What are my installation id and installation key used for?
Enter your installation key:
Retrieve an installation key using a valid email at https://bitwarden.com/host. For more information, see What are my installation id and installation key used for?
Enter your region (US/EU):
Enter US or EU depending on the cloud server you will use to license paid features, only applicable if you're connecting a self-hosted account or organization to a paid subscription.Do you have a SSL certificate to use? (y/n)
If you already have your own SSL certificate, specify
yand place the necessary files in theC:\Bitwarden\bwdata\ssl\<your_domain>directory. You will be asked whether it is a trusted SSL certificate (y/n). For more information, see Certificate Options.Alternatively, specify
nand use the self-signed SSL certificate? option, which is only recommended for testing purposes.Do you want to generate a self-signed SSL certificate? (y/n):
Specify
yto have Bitwarden generate a self-signed certificate for you. This option is only recommended for testing. For more information, see Certificate Options.If you specify
n, your instance will not use an SSL certificate and you will be required to front your installation with an HTTPS proxy, or else Bitwarden applications will not function properly.
Post-install configuration
Configuring your environment can involve making changes to two files; an environment variables file and an installation file:
Environment variables (required)
Some features of Bitwarden are not configured by the bitwarden.ps1 Cmdlet. Configure these settings by editing the environment file, located at \bwdata\env\global.override.env. At a minimum, you should replace the values for:
Bash... globalSettings__mail__smtp__host=<placeholder> globalSettings__mail__smtp__port=<placeholder> globalSettings__mail__smtp__ssl=<placeholder> globalSettings__mail__smtp__username=<placeholder> globalSettings__mail__smtp__password=<placeholder> ... adminSettings__admins= ...
Replace globalSettings__mail__smtp...= placeholders to connect to the SMTP mail server that will be used to send verification emails to new users and invitations to organizations. Adding an email address to adminSettings__admins= will provision access to the System Administrator Portal.
After editing global.override.env, run the following command to apply your changes:
Bash.\bitwarden.ps1 -restart
Installation file
The Bitwarden installation script uses settings in .\bwdata\config.yml to generate the necessary assets for installation. Some installation scenarios (such as installations behind a proxy with alternate ports) may require adjustments to config.yml that were not provided during standard installation.
Edit config.yml as necessary and apply your changes by running:
Bash.\bitwarden.ps1 -rebuild
Start Bitwarden
Once you have completed all previous steps, start your Bitwarden instance by running the following command:
Bash.\bitwarden.ps1 -start
note
The first time you start Bitwarden it may take some time as it downloads images from Docker Hub.
Verify that all containers are running correctly:
Bashdocker ps
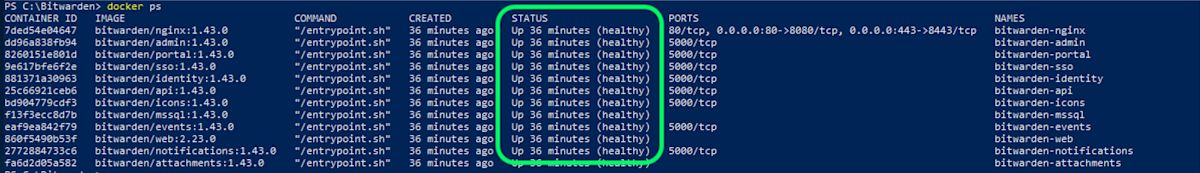
Congratulations! Bitwarden is now up and running at https://your.domain.com. Visit the web vault in your web browser to confirm that it’s working.
You may now register a new account and log in. You will need to have configured smtp environment variables (see Environment Variables) in order to verify the email for your new account.
tip
Once deployed, we recommend regularly backing up your server and checking for system updates.
Next Steps:
If you are planning to self-host a Bitwarden organization, see self-host an organization to get started.
For additional information see self hosting FAQs.
Start Docker on boot
Docker Desktop will only automatically start on boot if you have a logged-in RDP session. To start Docker Desktop on boot regardless of whether there is a user logged in:
warning
Docker Desktop may take up to 15 minutes after boot to fully start and for containers to be accessible from the network.
Open Task Scheduler and select Create Task... from the Actions menu.
Configure the task with the following security options:
Set the task to use the created
Bitwardenuser account.Set the task to Run whether user is logged on or not.
Select the Triggers tab and create the following trigger:
From the Begin the task dropdown, select At startup.
In the Advanced settings section, check the Delay task for: checkbox and select 1 minute from the dropdown.
Select the Actions tab and create the following action:
In the Program/script input, specify
"C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\frontend\Docker Desktop.exe".
Select OK to finish creating the scheduled task.
Script commands reference
The Bitwarden installation script (bitwarden.ps1) has the following commands available. All command must be prefixed with a switch (-), for example .\bitwarden.ps1 -start:
Command | Description |
|---|---|
-install | Start the installer. |
-start | Start all containers. |
-restart | Restart all containers. |
-stop | Stop all containers. |
-update | Update all containers and the database. |
-updatedb | Update/initialize the database. |
-updaterun | Update the run.ps1 file. |
-updateself | Update the installation script. |
-updateconf | Update all containers without restarting the running instance. |
-uninstall | Before this command executes, you will be prompted to save database files. |
-renewcert | Renew certificates. |
-rebuild | Rebuild generated installation assets from |
-help | List all commands. |